Read more about the pictures at top; the rock carving Sigurdsristning at Sim1 Travels
The Viking Age
| The Viking Age is the name of the period between 750 and 1100 AD in Scandinavia. The raid of Lindisfarne year 793 AD and the Battle of Stamford Bridges in 1066, where the Norwegian King Harald Hardrada (Harold III of Norway) was killed, are often used as the starting and ending points of the era. During this time Scandinavian traders and warriors traded and explored – and sometimes raided – most parts of Europe, south-western Asia, northern Africa and even north-eastern North America. |  |
Where
Geographically, a “Viking Age” may be assigned not only to the Scandinavian lands (modern Denmark, and southern Norway and Sweden and parts of Finland), but also to territories under North Germanic dominance, mainly Scotland, the Isle of Man and Ireland.
Viking navigators opened the road to new lands to the north and to the west, resulting in the colonization of Iceland, Greenland, Shetland, Orkney and the Farö Islands. The Vikings were actually just a small minority of the population in Northern Europe. Most people there were farmers or farmers’ thralls (slave).
The word Viking might come from the Old Norse word, vík, meaning “bay,” “creek,” or “inlet,” and to go out at the sea and go in a bay or “vik” to plunder or trade was called: “go viking”. Another explanation is that the term comes from old English, wíc “trading city” (Latin vicus, “village”). The medieval Scandinavian and northern Germany population, in general, is more properly referred to as Norse. |  |
Facts
Some facts that might ruin some myth of yours:
- The vikings did not have horns on their helmets, during Bronze Age horned helmet might have been used as a ceremonial tool.
- The legal systems throughout the medieval Nordic world were sophisticated and complex, and several law codes contain the phrase ‘with law shall the land be built’.
- Human skulls was not used as drinking vessels. The myth probably comes from a miss-translation of skål (bowl) to skalle (head) and we swedes toast with the word “Skål” when we drink ( from a bowl (skål) originally)
- The Old Norse Gods were not regarded as immortal
- While some Vikings clearly deserved their reputation as ‘wolves of war’, others lived peaceful existences – farming, trading and integrating across the four continents that they settled.
- Christian monks and other clergy was first to write down the Norse religion.
- The Vikings living in England had reputation of excessive cleanliness, due to their custom of bathing once a week.
Map from Wikipedia
Miklagård / Istanbul
Note that Istanbul (located south of Black Sea, in present Turkey) of today had a Norse name for centuries: Miklagarðr / Miklagård which is old Norse / Scandinavian for “Large Trading-place”. Later it was called Constantinople (after the king Konstantin I). It was called Istanbul after 1931. It had a strategic position on the historic Silk Road.


Ásatrú or the Norse Religion for Dummies
The following text is about the myth and believes – a religion – that dominated Northern Europe until about a thousand years ago, before Christianity was enforced in the region.
It is compiled by me Åke.
Norse Religion was an ethnical religion, like Hinduism and Judaism, not a founded one like Buddhism,
Christianity or Islam, which means that it is difficult to find a systematic doctrine in it. The Norse religion wasn’t a church. It had no pope and no written book how to behave. In general, ethnical religion is practice first and
theory second, if at all; it is not so much something to believe in as something to do.
Click here for a more comprehensive article at Wikipedia if you have plenty of time.
Or read this comprehensive text by Gunnar Gällmo LINK
Introduction
The religion
Old Norse religion was polytheistic, meaning there where various gods and goddesses. It was rooted in ritual practice and oral tradition and was not a “founded” religion like Christianity or Islam. Old Norse religion was fully integrated with other aspects of Norse life. The primary religious ritual was blót (sacrifice) at which animals were slaughtered and their blood sprinkled on the altars or other appropriate places.
A child was accepted into the family via a ritual of sprinkling with water (Old Norse ausa vatni)

In the beginning it was a big gap or abyss
This was before the earth, heaven and sea where created. Before the Gods where born it was a cold icy world in the north and burning in the south. When the heat meet the ice and drops where made.
The first drop was shaped into a giant; Ymer. When he slept a man and a woman grow out of his left armpit and his left foot got a son with his right.
Only one God has existed forever, he was Called Allfather and also had eleven other names. Also long before the earth was created, the World Tree –Yddrasil existed. That tree link all of the nine worlds.
The Gods and Goddesses
Thor had a hammer ”Mjölner” to fight and work with. The lightning from the sky came when Thor hits with his hammer. He had bucks (he-goat) instead of horses in front of his wagon. He was very strong, hot-tempered but more “human” than Oden. Not as clever as the other Gods but brave and maybe foolish.
One time he almost had the whole world to tip over. In a fight with the Midgårdsormen he grabbed the snake by the tail. The snake took a bite in the disc of the world and Thor pulled. He pulled so hard that the world almost tipped over. A little bit foolish but he was the most popular God. The most important of Vanerna was Frej: the Fertility God. The Swedish word “frö”; seed comes from Frej.Viking sacrificed to the Gods at special places outdoors; in groves and at stones. The most used burial method was cremation sometimes along with cows, horses, pigs and pets, usually dogs.
Classes of Æsir and Vanir
The Gods in old Norse religion was divided in two different classes: the Aesir and the Vanir. The Aesir were much connected to power and warfare, the Vanir to fertility.

Æsir
Oden was the supreme God of ásatrú . His father was Burr, who was son of Búri, who came into being when the primeval cow Audhhumbla licked some frost-covered, salty stones. Had two brothers – Hoenir and Loki.
Oden’s wife was Frigg, but as supreme God he had a lot of children and was not quite monogamous. As lord of the battle-field, he was the chief war-god, but not the only one. God of poetry as well as of warfare.
Tyr
God of warfare and battle. He was a son of either Oden or the giant Hymir.
Tyr was the bravest of all the Gods. He lost his right hand when the monstrous wolf Fenir bite it off. Tyr volunteered to put it in the terrifying gap, making possible for the other Gods to tie Fenir up by the chain Gleipnir.
Heimdallr
He is the guardian of the Gods Asgard, and will blow the Gjallarhorn if danger approaches. He was called the “White God” and is said to be born of nine mothers – possibly nine female giants who turned the world-mill – and thereby created him – or maybe the nine daughters of the sea-god Aegir, thus the waves of the sea, from which he was born.
He was also the guardian of the rainbow Bifrost
Loke
God of mischief, lying, deception and tricks. Also a considered a Giant. A son of Fárbauti and Nál. Unclear relations to Odin, probably Odin’s blood brother.
Loki was the father – and in one instance the mother – of many evil creatures, men and monsters like the three most important:
- Jörmungandr, the sea serpent
- Fenrir the giant wolf preordained to slay Odin at the time of Ragnarök
- Hel, ruler of the realm of the dead.
Because of his ill doing the Gods bound Loki to the rock. Then they tied a serpent above him, dripping poison onto his face. Loki´s wife Sigyn gathers the poison in a bowl, but sometimes she has to empty the bowl and when the poison drips onto Loki, he is in pain, causing the earthquakes when pulling hard to get loose.
Delling
Was the God of the dawn. By Nótt (night), he was the father of Dagr (day). He was Nótt´s third husband.
Dagr
God of the daytime, son of Delling
Mimer
Counsellor of the Gods, said to be wisest of aesir.
Aegir
God of the sea, the power of the ocean. His wife was Ran. They had nine daughters – called the billow maidens – who may have been identical with the nine mothers of Heimdallr. Their names were Bára, Bloðughadda, Bylgja, Duva, Himinglæva, Hefring, Hrönn, Kólga and Unnr and the names reflect different types of waves of the sea.
Aegir was brother to Loki and Kari and rather unpopular among the Viking, due to his way of making waves that made ship capsize.
Thor
God of thunder and battle. Thor is a straightforward God, not necessarily the wisest or most intelligent. Thor was the son of Oden and Jord (Earth) Thor travelled in a chariot drawn by goats, the sounds of thunder comes from him racing his vagon. The flash of lightning comes from the short-handled war hammer, Mjollnir, which, when thrown at a target, returned magically to the him.
Tanngrisnir and Tanngnjóstr
He had a simple way of righting wrongs: if it moves – kill it!
The evil God/Giant Loki knew that, so he tricked Thor several times to do some damage!
When the World Comes to an End
If you want alternative descriptions to the Apocalypse, Armageddon, Pralaya, Dharmasastra or End Of Time, you should read about Ragnarök, the Norse mythology version. Heavy Stuff!
Read more about Norse religion at wikipedia.
Runestones
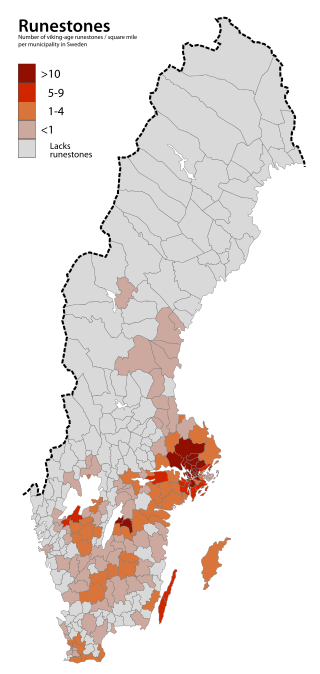
A runestone is typically a raised stone with a runic inscription, but the term can also be applied to inscriptions on boulders and on bedrock. The tradition began in the 4th century and lasted into the 12th century, but most of the runestones date from the late Viking Age. Most runestones are located in Scandinavia and in the counties of Uppland (1400) and Södermanland (400).
The picture to the right show where runestone are found in Sweden.
A majority, 94%, are raised in memory of men, who died at home. The most famous runestones that tell of foreign voyages are about 10% of all runestones and they were raised in usually memory of those not having returned from Viking expeditions.
You can see on the map above in this page the Vikings traveled far away from home, often to Miklagård (Constantinople, today Istanbul) to making business; trading with furs etc .


Read more about Rune-stone of Rök at Sim1 Travels
The Runic Alphabet
The majority of the run-rows found begin with the characters for F, u, Þ, a, r and K. That is the reason why it is called the Futhark alphabet. There are several version of this alphabet used in carving in a Runestone.
1. Older Futhark

The older Futhark consists of 24 runes. It is also called the Proto-Norse or Germanic futhark. One example of this on the oldest runestones found; Kylver stone, in Gotland, Sweden. Its from around 400 BC.
2. The Younger Futhark
picture
3. The Anglo-Saxon runes

